Azure IPAM
Note
While still maintained for now, Azure IPAM is considered legacy and is not compatible with AKS clusters created in Bring your own CNI mode. The recommended way to install cilium on AKS are Bring your own CNI or Azure CNI Powered by Cilium.
The Azure IPAM allocator is specific to Cilium deployments running in the Azure cloud and performs IP allocation based on Azure Private IP addresses.
The architecture ensures that only a single operator communicates with the Azure API to avoid rate-limiting issues in large clusters. A pre-allocation watermark allows to maintain a number of IP addresses to be available for use on nodes at all time without requiring to contact the Azure API when a new pod is scheduled in the cluster.
Architecture
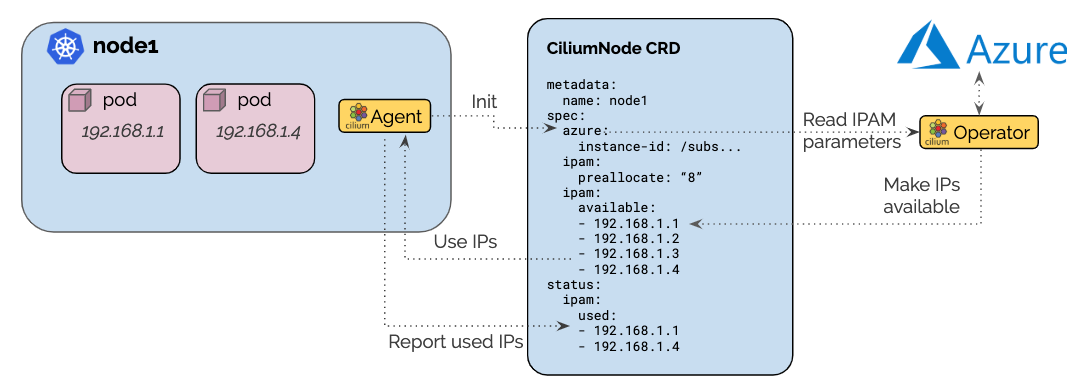
The Azure IPAM allocator builds on top of the CRD-backed allocator. Each node
creates a ciliumnodes.cilium.io custom resource matching the node name when
Cilium starts up for the first time on that node. The Cilium agent running on
each node will retrieve the Kubernetes v1.Node resource and extract the
.Spec.ProviderID field in order to derive the Azure instance ID.
Azure allocation parameters are provided as agent configuration option and are
passed into the custom resource as well.
The Cilium operator listens for new ciliumnodes.cilium.io custom resources
and starts managing the IPAM aspect automatically. It scans the Azure instances
for existing interfaces with associated IPs and makes them available via the
spec.ipam.available field. It will then constantly monitor the used IP
addresses in the status.ipam.used field and allocate more IPs as needed to
meet the IP pre-allocation watermark. This ensures that there are always IPs
available
Configuration
The Cilium agent and operator must be run with the option
--ipam=azureor the optionipam: azuremust be set in the ConfigMap. This will enable Azure IPAM allocation in both the node agent and operator.In most scenarios, it makes sense to automatically create the
ciliumnodes.cilium.iocustom resource when the agent starts up on a node for the first time. To enable this, specify the option--auto-create-cilium-node-resourceor setauto-create-cilium-node-resource: "true"in the ConfigMap.It is generally a good idea to enable metrics in the Operator as well with the option
--enable-metrics. See the section Running Prometheus & Grafana for additional information how to install and run Prometheus including the Grafana dashboard.
Azure Allocation Parameters
The following parameters are available to control the IP allocation:
spec.ipam.min-allocateThe minimum number of IPs that must be allocated when the node is first bootstrapped. It defines the minimum base socket of addresses that must be available. After reaching this watermark, the PreAllocate and MaxAboveWatermark logic takes over to continue allocating IPs.
If unspecified, no minimum number of IPs is required.
spec.ipam.pre-allocateThe number of IP addresses that must be available for allocation at all times. It defines the buffer of addresses available immediately without requiring for the operator to get involved.
If unspecified, this value defaults to 8.
spec.ipam.max-above-watermarkThe maximum number of addresses to allocate beyond the addresses needed to reach the PreAllocate watermark. Going above the watermark can help reduce the number of API calls to allocate IPs.
If let unspecified, the value defaults to 0.
Operational Details
Cache of Interfaces, Subnets, and VirtualNetworks
The operator maintains a list of all Azure ScaleSets, Instances, Interfaces, VirtualNetworks, and Subnets associated with the Azure subscription in a cache.
The cache is updated once per minute or after an IP allocation has been performed. When triggered based on an allocation, the operation is performed at most once per second.
Publication of available IPs
Following the update of the cache, all CiliumNode custom resources representing nodes are updated to publish eventual new IPs that have become available.
In this process, all interfaces are scanned for all available IPs. All IPs
found are added to spec.ipam.available. Each interface is also added to
status.azure.interfaces.
If this update caused the custom resource to change, the custom resource is
updated using the Kubernetes API methods Update() and/or UpdateStatus()
if available.
Determination of IP deficits or excess
The operator constantly monitors all nodes and detects deficits in available IP addresses. The check to recognize a deficit is performed on two occasions:
When a
CiliumNodecustom resource is updatedAll nodes are scanned in a regular interval (once per minute)
When determining whether a node has a deficit in IP addresses, the following calculation is performed:
spec.ipam.pre-allocate - (len(spec.ipam.available) - len(status.ipam.used))
For excess IP calculation:
(len(spec.ipam.available) - len(status.ipam.used)) - (spec.ipam.pre-allocate + spec.ipam.max-above-watermark)
Upon detection of a deficit, the node is added to the list of nodes which require IP address allocation. When a deficit is detected using the interval based scan, the allocation order of nodes is determined based on the severity of the deficit, i.e. the node with the biggest deficit will be at the front of the allocation queue. Nodes that need to release IPs are behind nodes that need allocation.
The allocation queue is handled on demand but at most once per second.
IP Allocation
When performing IP allocation for a node with an address deficit, the operator first looks at the interfaces already attached to the instance represented by the CiliumNode resource.
The operator will then pick the first interface which meets the following criteria:
The interface has addresses associated which are not yet used or the number of addresses associated with the interface is lesser than maximum number of addresses that can be associated to an interface.
The subnet associated with the interface has IPs available for allocation
The following formula is used to determine how many IPs are allocated on the interface:
min(AvailableOnSubnet, min(AvailableOnInterface, NeededAddresses + spec.ipam.max-above-watermark))
This means that the number of IPs allocated in a single allocation cycle can be
less than what is required to fulfill spec.ipam.pre-allocate.
IP Release
When performing IP release for a node with IP excess, the operator scans the interface attached to the node. The following formula is used to determine how many IPs are available for release on the interface:
min(FreeOnInterface, (TotalFreeIPs - spec.ipam.pre-allocate - spec.ipam.max-above-watermark))
Node Termination
When a node or instance terminates, the Kubernetes apiserver will send a node
deletion event. This event will be picked up by the operator and the operator
will delete the corresponding ciliumnodes.cilium.io custom resource.
Required Privileges
The following Azure API calls are being performed by the Cilium operator. The Service Principal provided must have privileges to perform these within the scope of the AKS cluster node resource group:
Note
The node resource group is not the resource group of the AKS cluster. A single resource group may hold multiple AKS clusters, but each AKS cluster regroups all resources in an automatically managed secondary resource group. See Why are two resource groups created with AKS? for more details.
Metrics
The metrics are documented in the section IPAM.